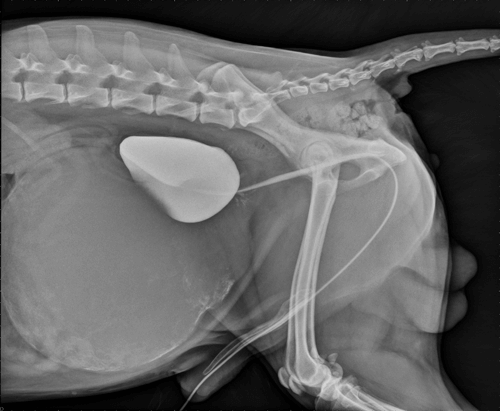
These occur uncommonly in male dogs of medium or large breeds. This video presents a case of very large paraprostatic cyst that could be confused with the bladder.

Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia In Dogs And Cats Reproductive System Msd Veterinary Manual
Paraprostatic cysts result from embryologic remnants of the female reproductive tract found in males that become fluid-filled.

. Paraprostatic cysts are large cysts that lie next to the prostate gland and are usually connected to the prostate by a stalk. The bladder is flushed with saline and this sample is saved. The prostate is subsequently massaged per rectum for.
Cysts occurred predominantly in older large breed dogs mean age 8 years range 311 years. The ultrasonographic features of paraprostatic cysts in nine dogs are described along with historical clinical surgical and pathologic findings. A retrograde urogram might also allow the localization of the bladder.
Two of the dogs were found to have concurrent benign prostatic hyperplasia while the third had chronic active prostatitis. The catheter is then withdrawn so that the end is caudal to the prostate. Cysts closed sacs of fluid can develop on or around the prostate causing enlargement of the gland which can lead to difficulty in urination and bowel function.
And paraprostatic close to the prostate cysts that are cavitating fluid-filled lesions with a. Prostatic cysts affect male dogs commonly larger dogs anywhere between the age of one and a half to twelve years. The most common presenting complaints were depression inappetance stranguria tenesmus and bloody.
Predisposing factors General Older intact males large breed dogs. Affiliation 1 Département de pathologie et microbiologie Faculté de médecine vétérinaire Université de Montréal Saint-Hyacinthe Québec. Large cysts may result in abdominal distention and.
Authors C Girard 1 J Despôts. If the dog will not ejaculate material for cytologic and microbiologic examination can be obtained by prostatic massage. Paraprostatic cysts result from embryologic remnants of the female reproductive tract found in males that become fluid-filled.
Mineralized paraprostatic cyst in a dog. The identification of paraprostatic cysts can usually be made with contrast radiography by accurately delineating where the urinary bladder is in relationship to the cyst. Paraprostatic cysts are rare findings present occasionally with concomitant benign prostatic hyperplasia in older large breed intact male dogs 1 2.
Paraprostatic cyst in one dog. Prostatic retention cysts - concurrent prostatic disease wide based intimacy of bladder neck to prostate. Using aseptic technique the bladder is catheterized and all urine removed.
Symptoms of Paraprostatic Cysts Prostatic Cysts in Dogs may include. Paraprostatic cysts in two dogs. Mineralized paraprostatic cyst in a dog Can Vet J.
The most common presenting complaints were depression inappetance stranguria tenesmus and bloody penile discharge. The paraprostatic cyst is not a common disease of the prostate gland. Paraprostatic cysts - unknown congenital only fascial attachment to prostate.
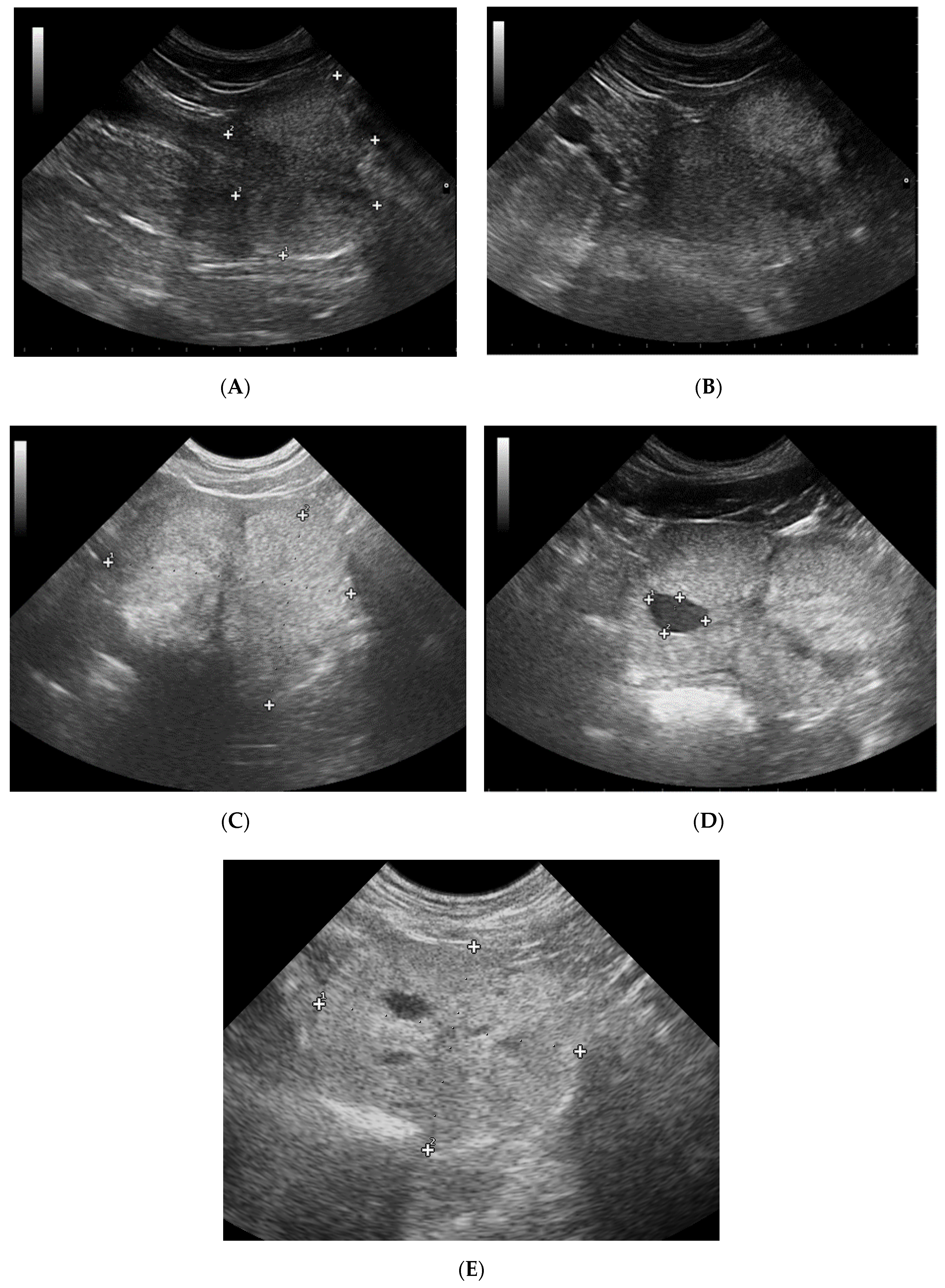
An abdominal ultrasound confirmed the radiographic diagnosis and also to evaluate the number and size of the cysts and eventually to guide aspiration of those cysts. Cysts occurred predominantly in older large breed dogs mean age 8 years range 311 years. Prostatic cysts are generally rare and benign non-cancerous.
Prostatic cysts in the dog have several associations. A paraprostatic cyst or several cysts is the major hypothesis. Paraprostatic cysts do not open into the urethra as normal prostatic ducts do.
Fluid-filled lesions with a distinct capsule sac-like enclosure. Straining to defecate pass stool Straining to urinate Abdominal distention Swelling in the perineal area area under the anus Blood in the urine Discharge from the penis that is either bloody cloudy yellow or clear Occasionally an animal may experience urinary incontinence. All three animals had paraprostatic cysts originating within the abdominal cavity and extending caudally through the pelvic canal causing perineal swelling.
A description is given of the history clinical features surgery outcome and pathology of 12 dogs with discrete prostatic cysts over 50 ml in volume. The signs are similar to those seen with other types of prostatic enlargement and usually become apparent only when the cyst reaches a size sufficient to cause pressure on adjacent organs. Prostatic cysts usually result from an obstruction of prostatic ducts and fluid retention within the prostatic parenchyma.
Prostatic and paraprostatic periprostatic cysts are fluid-filled pockets associated with the prostate. The dogs were middle-aged and presented with either urinary or alimentary signs or both. Paraprostatic cysts are fluid-filled cavities originating from the prostate and expanding beyond the prostate when they are of large size.
Changes in the cells brought on by hormonal changes. Osseous metaplasia paraprostatic cyst prostatic hyperplasia. Annotated video without sound 212.
The cat has only a rudimentary prostate gland so these. There are usually multiple cavitary areas within the gland which potentially. This entry was posted by Marc-Andre dAnjou.
The signs are similar to those seen with other types of prostatic enlargement and usually become apparent only when the cyst reaches a size sufficient to cause pressure on adjacent organs. The present report describes in detail the clinical status radiological haematological and histological findings in a canine patient. These fluid-filled cysts are often located on or extending from the external margins of the prostate but their exact origin is uncertain.
Following non-standard surgical intervention ureterocolonic anastomosis the status of the patient was studied for a period of eight months. Large cysts may result in abdominal distention and must be. To access this post you must purchase Mastering Ultrasound in Dogs and Cats Small Animal Ultrasonography PREMIUM 2 years or Abdominal diseases Section 1 of Mastering Ultrasound.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia This disorder develops in older intact male dogs and is a natural result of aging and hormonal influence on the prostate gland. The cyst was usually palpable in the posterior abdomen as a smooth non-painful mass readily demonstrable on contrast. Retention cysts within the prostate that are cavitating capable of forming a cavity in the tissue or organ.
All prostatic cysts are more likely to occur in intact unneutered male dogs.
Animals Free Full Text B Mode And Doppler Ultrasonographic Findings Of Prostate Gland And Testes In Dogs Receiving Deslorelin Acetate Or Osaterone Acetate Html
![]()
A Case Of Paraprostatic Cyst In A Dog Vetpixel Clinical Case
He Really Should Have Studied For His Prostate Exam Samson Hardy A Labrador Retriever With Prostatitis Lawndale Veterinary Hospital

Read About Reproduction In This Article By Thurid Freitag And More
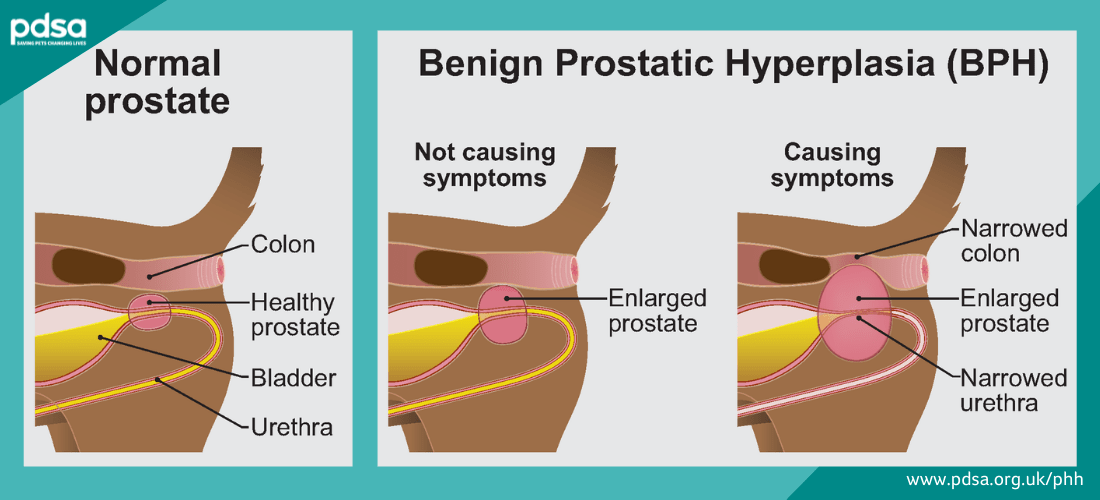
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Bph In Dogs Pdsa

Series 3 The Birds The Bees Of Veterinary Reproductive Clinical Sonography Sonopath

Inguinal Herniation Of A Mineralized Paraprostatic Cyst In A Dog Abstract Europe Pmc
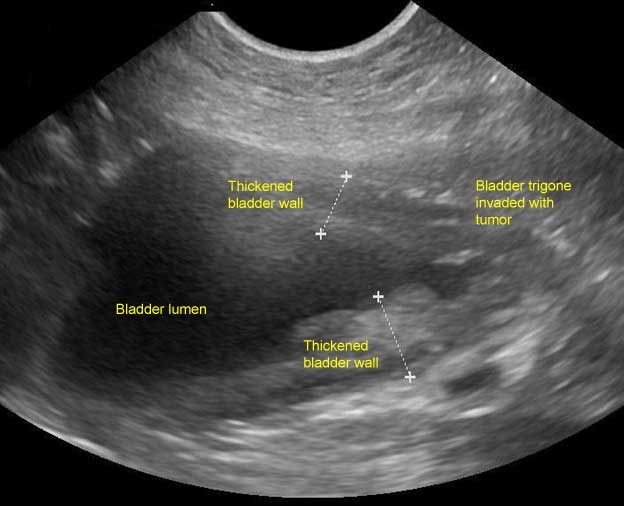
Enjoy This Oncology Article By Sandra M Axiak And Astrid Bigio
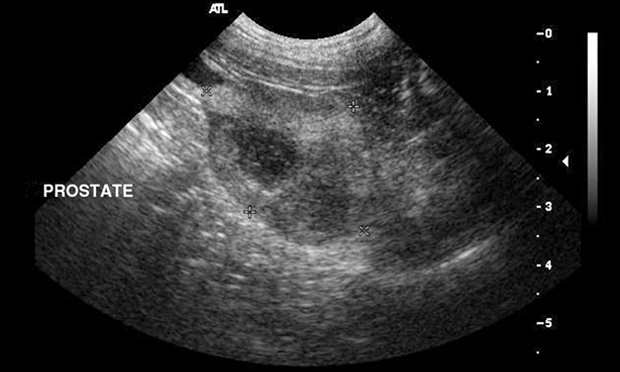
Prostatic Disease Clinician S Brief

Prostatic Disease Clinician S Brief

Enjoy This Oncology Article By Sandra M Axiak And Astrid Bigio

Pdf Cystic Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia In A Dog Semantic Scholar

Series 3 The Birds The Bees Of Veterinary Reproductive Clinical Sonography Sonopath

Animal Surgical Center Of Michigan Veterinarian In Flint Mi
Urinary Cyst In A Dog Why You Should Measure Creatinine In Prostatic Cyst Fluid Vet Practice Support

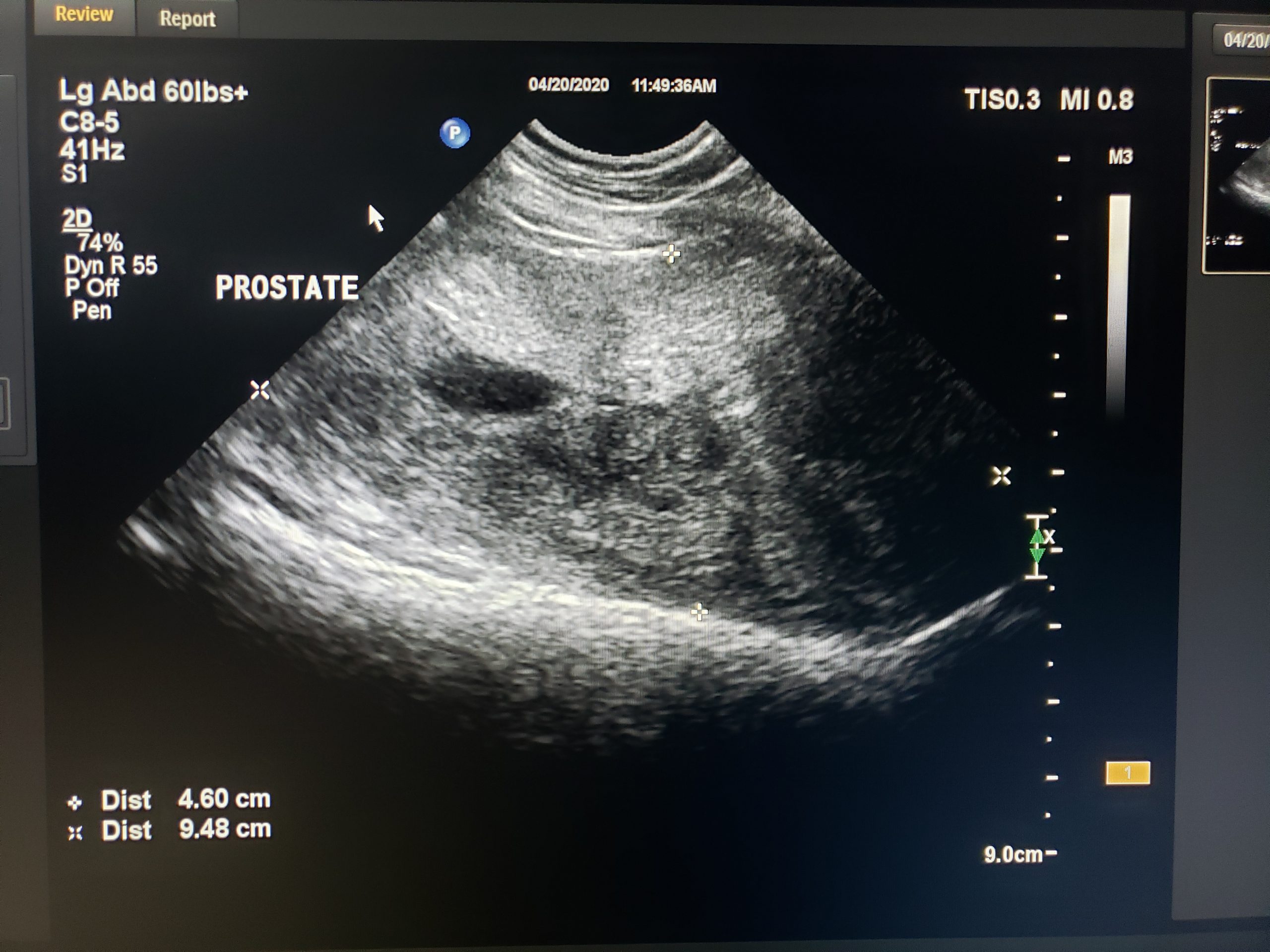
Ultrasound Images Of Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia With Intraprostatic Download Scientific Diagram

Prostatic Diseases In Small Animals Reproductive System Msd Veterinary Manual